In class we presented a disease that is very deadly called Adrenoleukodystrophy (ADL). This presentation interested a lot of people and I learned a lot. We had both a powerpoint and a poster board presentation. I shared the powerpoint with you but heres a link just in case.
https://docs.google.com/a/lajunta.k12.co.us/presentation/d/1Horz8qngkocDChBpAz0FJe5K1237yKsgcWlfR5EgRGU/edit#slide=id.p
Madara's Epic Battle Between Anatomy and Physiology
Friday, March 15, 2013
Sheep Lab/ Brain blog
Early in the quarter we did a sheep brain lab. We disected the brain into bread slices to find the different parts of the brain. This included the exterior parts parietal lobe, frontal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe, an the cerebellum.
The parietal lobe of the brain is located on the upper back of the brain. The parietal lobe is used for many different things. It is used to integrate different sensory information throughout your whole body. This part of the brain also contains the primary sensory cortex which is used to determine different senses. This part of the brain also is what helps to keep us from walking into things. After injury of the parietal lobe you could have trouble locating body parts, or unable to recognize those parts.
The frontal lobe is the upper front of the brain.It is right in front of the parietal lobe. This part of the brain is the biggest of them all. This is used for planning, memory, organization, problem solving, impulse control, decision making, selective attention, and controlling our behavior and emotions. The left frontal lobe focuses mostly on language and speech.Problems after injuring this part of the brain would include emotions, impulse control, language, memory, and sexual and social behavior.
The temporal lobe is right below the parietal and frontal lobe. This lobe is used to process and recognize sound so you understand what people are saying. This would also include understanding the speech that those people are using. This part also has different aspects to memory. With an injury to the temporal lobe the side effects could include hearing loss, language problems, and even being able to recognize someone if bad enough.
The occipital lobe is right behind the temporal lobe. This lobe is the eyesight lobe to get us seeing. With this it receives and processes information through visuals. It also helps us perceive different shapes and colors.With an injury to this part of the brain our visuals could be impaired or we could have deceptive visuals with shapes and/or colors..
The cerebellum is right below the occipital lobe.This is used for balance, movement, and coordination. With out the cerebellum we would all be walking around falling a lot, and running into things. It also allows to stand up straight, keep our balance, and literally move around. With an injury to the cerebellum you could have uncoordinated movement, loss of muscle tone, or even unsteady gait.




The parietal lobe of the brain is located on the upper back of the brain. The parietal lobe is used for many different things. It is used to integrate different sensory information throughout your whole body. This part of the brain also contains the primary sensory cortex which is used to determine different senses. This part of the brain also is what helps to keep us from walking into things. After injury of the parietal lobe you could have trouble locating body parts, or unable to recognize those parts.
The frontal lobe is the upper front of the brain.It is right in front of the parietal lobe. This part of the brain is the biggest of them all. This is used for planning, memory, organization, problem solving, impulse control, decision making, selective attention, and controlling our behavior and emotions. The left frontal lobe focuses mostly on language and speech.Problems after injuring this part of the brain would include emotions, impulse control, language, memory, and sexual and social behavior.
The temporal lobe is right below the parietal and frontal lobe. This lobe is used to process and recognize sound so you understand what people are saying. This would also include understanding the speech that those people are using. This part also has different aspects to memory. With an injury to the temporal lobe the side effects could include hearing loss, language problems, and even being able to recognize someone if bad enough.
The occipital lobe is right behind the temporal lobe. This lobe is the eyesight lobe to get us seeing. With this it receives and processes information through visuals. It also helps us perceive different shapes and colors.With an injury to this part of the brain our visuals could be impaired or we could have deceptive visuals with shapes and/or colors..
The cerebellum is right below the occipital lobe.This is used for balance, movement, and coordination. With out the cerebellum we would all be walking around falling a lot, and running into things. It also allows to stand up straight, keep our balance, and literally move around. With an injury to the cerebellum you could have uncoordinated movement, loss of muscle tone, or even unsteady gait.

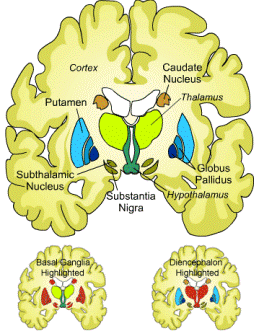
We also focused on the interior of the brain. When had to determine different parts. These included the cortex, putamen, subthalamic nucleus, Caudate nucleus, thalamus, global pallidus, hypothalamus, and substantia nigra.
The cortex is located on the top left of the brain.
The putamen is located right below the cortex.
The subthalamic nucleus is right below the putamen.
The caudate nucleus is on the top right of the brain above the start of the hypothalamus.
The thalamus is below the caudate nucleus.
The global pallidus is on both sides of the brain in about the center of each side.

THESE ARE THE PICTURES FROM OUR LAB



HERE IS A VIDEO
Friday, December 21, 2012
Muscular System
Why is the Muscular System so important? Without the muscular system we would not be able to move. Without muscle humans would be non-existent.
Functions of the Muscular system
Muscular tendons stabilize joints so that the joints won't move out of place. This would make your bones pop out of place if you bent your arm without these tendons. Muscle helps us stand up, and practically fight gravity. If we didn't have the muscle helping us stand up we would fall from gravity. Moving the skeleton is probably the most useful function that muscle has because without muscle moving our bones how would we move. And the last main useful function that a muscle has is heat production because it obviously keeps us warm.
Types of Muscles
Smooth:
This muscle is involuntary which means its automatically controlled without thinking about it. An example of a smooth muscle is the esophagus. It is used to force food down to you stomach. We never think about it, but it always happens.
Cardiac:
Cardiac muscle is also an involuntary type of muscle. The cardiac muscle is the heart muscle that works on its own.
Skeletal:
The skeletal muscles are voluntary. This is because you do think about where your going or what you pick up. The skeletal muscles are what get you from place to another. The skeletal muscles are attached to the skeleton.
Bibliography
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q5MyCwatq6E
Cardiac:
Cardiac muscle is also an involuntary type of muscle. The cardiac muscle is the heart muscle that works on its own.
Skeletal:
The skeletal muscles are voluntary. This is because you do think about where your going or what you pick up. The skeletal muscles are what get you from place to another. The skeletal muscles are attached to the skeleton.
Structure of Skeletal Muscle
Fascia
The Fascia is only found in the skeletal muscle. This is the covering of the muscle and it becomes the tendons.
Myofibrals
The myofibrals are in all muscle because they muscle fibers. They are involved in muscle contraction.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q5MyCwatq6E
Wednesday, December 19, 2012
Bone Stucture
We did a whole unit of bones and I learned more about the skelatal system more than any other body system this semester. We had a number of different projects and activities to learn more about bone.
There are two different classification of bones. They are the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
Axial Skeleton
The axial skeleton consists of the skull bones, the neck, the rib cage, and the back vertebrae.
There are two different classification of bones. They are the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
Axial Skeleton
The axial skeleton consists of the skull bones, the neck, the rib cage, and the back vertebrae.
Appendicular Skeleton
The Appendicular Skeleton consists of, the shoulders, the limbs, and the hips
Classification of Bones: By Shape
There are four different types of bones which are long bones that are longer than they are wide such as the humorous, short bones that are cubed shaped bones of the wrist and ankle and bones that form within tendons, flat bones that are thin flattened and a bit curved, and irregular bones that are weird shaped.
Long Bones
Short Bones
Flat Bones
Irregular Bones
What are the functions of bones?
There are many different functions to bones and some of them are very obvious. The bones give support because it forms a frame the supports the body and protects soft organs. The bones also give protection by providing a frame for the brain, spinal cord, and vital organs so the are unlikely to get damaged. Movement is a very important thing for our body and the bones provide levers for muscles so we can move.Mineral storage is a huge thing that bones do because it makes the bones stronger. When you are little your parents always told you to drink alot of milk. This is because milk provides calcium and bones store calcium for strength. Bones also store phosphorus. Blood cell formation also happens in the bone. This is a process called hematopoiesis and it occurs within the marrow cavities of bone.
What are the Structures of Different Bones?
Long Bones
These bones consist of a diaphysis and an epiphysis. In the diaphysis there is a tubular shaft that forms the length and axis of long bones. This part of the bone is composed of compact bone that surrounds the medullary cavity. The medullary cavity is where yellow bone marrow or (fat) is stored. The epiphysis is the expanded ends of the long bones. The exterior of this part of bone is compact bone and then the interior is spongy bone. The joint surface on the tip of each side is covered with articular (hyaline) cartilage. There is a line that separates the epiphysis from the diaphysis call the epiphyseal line.
Sunday, November 4, 2012
Tattoos (Integumentary System)
Structure of Skin
In the integumentary system there are three major layers. The dermis, the epidermis, and the hypodermis are these three layers. Here are there functions and some of the parts of each layer.
The bottom layer of the epidermis is the basal layer. This layer is attached to the dermis and is the deepest epidermal layer. This layer has all of the youngest keratinocytes. Cells divide which gives this layer the name Stratum Germinativum.

The next layer is called the Prickly layer. This layer contains a weblike system of filaments attached to desmosomes. There are alot of Melanin granules and Langerhans' cells in this layer. It is also called the Stratum Spinosum.

The third layer is called the Granular Layer.This is a very thin layer where big changes in keratinocyte appearance happens. In this layer Keratohyaline and lamellated granules accumulate. This layer is also called Stratum Granulosum.

The fourth layer is called the clear layer. It is a clear layer that is superficial to the Granular Layer. It consists of a couple layers of dead keratinocytes. This layer is only present on think skin such as on the palm of your hand. This layer is also called the Stratum Lucidum.

The fifth and top layer is called the Horny Layer. It is by far the thickest taking up seventy five percent of the epidermis. Its functions include waterproofing, protection from abrasion and penetration, and rendering the body relatively insensitive to biological, chemical, and physical assaults. This layer is also called the Stratum Corneum.

The Dermis has two main layers
The next layer in the skin is called the Dermis. It is composed of two different main layers. This layer is made of strong, flexible connective tissue. The cells in it are fibroblasts, macrophages, and white and mast blood cells. The two layer of the Dermis are papillary and reticular.
The top layer in the Dermis is called the papillary layer. It consists of Areolar connective tissue with collagen and elastic fibers. It has piglike things called dermal papillae which has capillary loops, Meissners corpuscles, and free nerve endings.

The bottom layer in the Dermis is called the Reticular Layer. This layer is eighty percent of all of skins thickness. It consists of collagen fibers which gives it strength and resiliency to the skin which makes it strong but also very elastic.

The Hypo Dermis is the last layer of skin and is very think. It is used for insulation and is made from adipose and areolar connective tissue.

Tattoos
Tattoos are always something that I've wondered about. How do they work? From my research the tattooist uses a machine that penetrates the skin with a need that travels 50 to 3000 times per minute. The ink that goes into the skin appears on the epidermis, but it is actually place in the Dermis. This is because the Dermis properties are alot more stable so the ink will not move. In fact there is hardly any fading through a lifetime.
The next layer is called the Prickly layer. This layer contains a weblike system of filaments attached to desmosomes. There are alot of Melanin granules and Langerhans' cells in this layer. It is also called the Stratum Spinosum.
The third layer is called the Granular Layer.This is a very thin layer where big changes in keratinocyte appearance happens. In this layer Keratohyaline and lamellated granules accumulate. This layer is also called Stratum Granulosum.
The fourth layer is called the clear layer. It is a clear layer that is superficial to the Granular Layer. It consists of a couple layers of dead keratinocytes. This layer is only present on think skin such as on the palm of your hand. This layer is also called the Stratum Lucidum.
The fifth and top layer is called the Horny Layer. It is by far the thickest taking up seventy five percent of the epidermis. Its functions include waterproofing, protection from abrasion and penetration, and rendering the body relatively insensitive to biological, chemical, and physical assaults. This layer is also called the Stratum Corneum.
Wednesday, September 5, 2012
Homeostasis
What is Homeostasis
When homeostasis is brought up what do you know about it? Well as I learned about it I figured out it was basically the consistency of different body conditions. What that means is it keeps the internal body in a constant condition no matter the external condition that surrounds it. This keeps the body in balance so that it will function right. For example if its hot outside your body will stay roughly 98.6 degrees or if its cold outside your body will still be 98.6 degrees.
Homeostasis with Different Body Systems
Digestive System: Homeostasis breaks down food and sends it to cells so they can function properly. If your cells don't function properly obviously something will go wrong.
Respiratory System: Homeostasis is what is used to move oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and blood. So as you can see this is what also keeps you breathing.
Urinary System: Homeostasis is what has the liver remove toxins from the blood and converts them into chemicals that can be removed from the body with the kidney. So obviously you don't want nasty wastes roaming around in your body.
Negative Feedback
Negative feedback in homeostasis is when receptors in the body detect when something is off balance or wrong with the homeostasis system. In turn this turns on an effector (something that causes a reaction) which then the reaction restores balance. When the response is enough to return the body back to balance, the receptor turns off.
An example of negative feedback is temperature control in the body. The hypothalamus the body temp monitor can identify any type of change in body temp. When you get cold it gets your body to shiver to raise your body temp and uses sweating to lower the temp of your body.
An example of negative feedback is temperature control in the body. The hypothalamus the body temp monitor can identify any type of change in body temp. When you get cold it gets your body to shiver to raise your body temp and uses sweating to lower the temp of your body.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)









